Ein moderner Shopware 6 Shop ist weit mehr als nur ein Online-Shop. Er ist eine leistungsfähige, flexible und langfristig wartbare E-Commerce-Plattform. Stefan Pilz hat sich darauf spezialisiert, Sho...
Stefan Pilz ist ein erfahrener freiberuflicher PHP-Entwickler und E-Commerce-Experte mit Sitz in Zypern. Über seine professionelle Portfolio- und Business-Website stefanpilz.ltd bietet er spezialisie...
In der dynamischen Technologielandschaft von Zürich, Bern und Basel zeichnet sich eine fundamentale Wende ab. Während die klassische Programmierung jahrelang durch Syntax, Debugging und manuelle Cod...
In der heutigen digitalen Landschaft stehen Unternehmen in Zürich, Bern und Basel vor der Herausforderung, Software schneller, sicherer und innovativer zu entwickeln. Während klassische KI-Tools wie...
In der dynamischen Technologielandschaft von Zürich, dem Herzen der Schweizer Innovation, bahnt sich ein fundamentaler Wandel an. Während die erste Welle der Künstlichen Intelligenz uns Werkzeuge b...
Mit dem Einzug der Industrie 4.0 hat das Laserschneiden einen technologischen Sprung gemacht. Statt nur ein Schneidverfahren zu sein, ist es heute Teil vollständig digitalisierter Produktionsketten. ...
Das Drahterodieren hat sich in den letzten Jahrzehnten zu einem unverzichtbaren Bestandteil der Präzisionsfertigung entwickelt. Moderne Maschinen kombinieren Hochpräzisionsmechanik, intelligente Ste...
Das Tieflochbohren ist ein hochspezialisiertes und anspruchsvolles Fertigungsverfahren, das immer dann zum Einsatz kommt, wenn das Verhältnis von Bohrtiefe zu Bohrungsdurchmesser (L/D-Verhältnis) se...
Das CNC-Drehen ist eines der ältesten, aber auch eines der modernsten Fertigungsverfahren zugleich. Obwohl der Grundgedanke seit Jahrhunderten unverändert blieb – ein rotierendes Werkstück wird m...
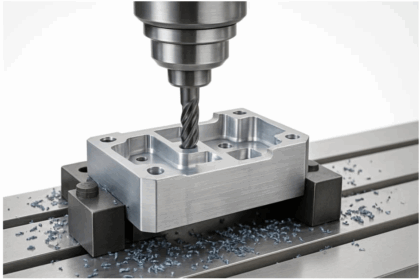
Das CNC-Fräsen ist eines der vielseitigsten Fertigungsverfahren der modernen Industrie. Eine zentrale Stärke besteht darin, dass eine große Bandbreite von Materialien verarbeitet werden kann – vo...